Unleashing Creativity: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Pens and Their Impact
3D pens have emerged as a revolutionary tool in the realm of creativity and innovation. With their ability to transform imagination into tangible, three-dimensional objects, these pens are not only capturing the interest of artists and designers but also inspiring hobbyists, educators, and engineers alike. But what exactly is a 3D pen, and how does it work? This article delves into the world of 3D pens, exploring their features, uses, and the impact they have on various fields.
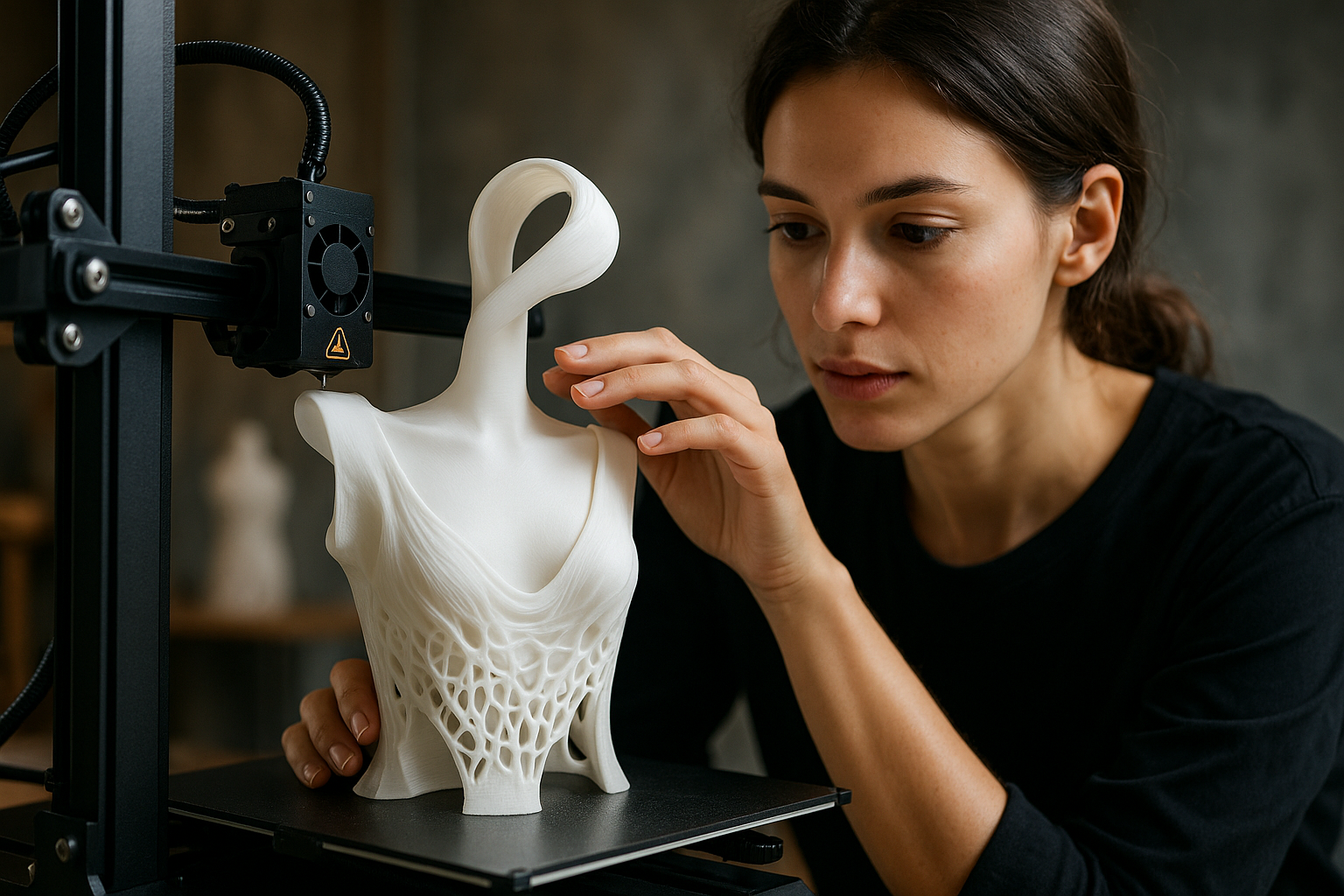

3D pens represent one of the most accessible entries into the world of three-dimensional creation. Unlike their larger cousins—3D printers—these handheld devices offer immediate creative gratification without complex software or lengthy printing times. Originally introduced to the consumer market in 2013, 3D pens have evolved from novelty gadgets into versatile tools used by artists, educators, designers, and hobbyists alike. Their ability to transform plastic filament into tangible objects has revolutionized how we conceptualize and create in three dimensions.
3D Pens Transforming Imagination into Reality
The transformative power of 3D pens lies in their ability to instantly materialize ideas. Unlike traditional art forms that work in two dimensions, 3D pens allow creators to build upward and outward, defying gravity and conventional artistic limitations. This immediate translation from thought to physical form has proven particularly valuable for visual thinkers who struggle to express spatial concepts through traditional mediums. Children with developing motor skills find 3D pens especially engaging as they provide tactile feedback while encouraging spatial reasoning. Professional artists have embraced these tools to create intricate sculptures, jewelry, and even functional prototypes that would be difficult to achieve through conventional methods.
Creating 3D Art with Precision and Technique
Mastering 3D pen artistry requires understanding both the technical aspects of the tool and developing specialized techniques. Temperature control is crucial—different filament types require specific heat settings for optimal flow and structural integrity. Artists typically begin with simple flat shapes on paper before lifting into three-dimensional space, using techniques like “air drawing” (creating structures that stand freely) and “layering” (building up thickness and strength). Advanced users employ techniques such as bridging (spanning gaps between anchor points) and scaffolding (creating temporary support structures). The learning curve varies, but most users can create basic three-dimensional objects within hours of practice, while complex artistic mastery may take months to develop.
Revolutionizing Education and Design Processes
Educational institutions have recognized the potential of 3D pens as powerful STEM teaching tools. In classrooms, these devices help students visualize complex geometric concepts, molecular structures, and architectural principles in tangible form. Engineering students use them for rapid prototyping of design concepts, while art programs incorporate them into mixed-media curricula. The hands-on nature of 3D pen creation engages kinesthetic learners who might struggle with abstract concepts when presented only in two dimensions. Professional designers have also incorporated these tools into their workflows, using them for quick concept modeling, design refinements, and creating physical representations that can be shared with clients before moving to more complex production methods.
From Plastic to Art: How 3D Pen Technology Works
The mechanics behind 3D pens involve sophisticated temperature control systems within a compact form factor. Most models use a heating element to melt plastic filament (typically ABS or PLA) to a precise temperature—usually between 130-240°C depending on the material. Motor-driven gears then push the melted plastic through a fine nozzle. Upon exposure to air, the extruded plastic cools and solidifies rapidly, allowing it to maintain whatever shape the user creates. Advanced models feature adjustable speed settings, temperature controls, and even LCD displays that provide real-time feedback. The filament itself comes in hundreds of colors, including specialty varieties that glow in the dark, change color with temperature, or incorporate wood, metal, or carbon fiber particles for unique visual and structural properties.
The Future of Creativity with 3D Pens and Emerging Applications
As 3D pen technology continues to evolve, we’re seeing integration with other creative technologies. Some artists combine 3D pen work with traditional 3D printing, using the pens to add custom details or repairs to printed objects. Others are experimenting with new materials, including biodegradable filaments made from plant-based sources like corn starch. The medical field has shown interest in specialized 3D pens that can “draw” with biocompatible materials for wound healing applications. In fashion, designers are creating intricate jewelry and textile embellishments that would be impossible with traditional manufacturing methods. As the technology becomes more refined, we can expect to see increasingly sophisticated applications across industries ranging from automotive prototyping to custom medical devices.
3D Pen Models and Cost Considerations
The market offers 3D pens across various price points and capability levels, from entry-level models to professional-grade tools. Understanding the options can help consumers make informed decisions based on their needs and budget.
| Model Category | Average Price Range | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level | $20-$40 | Basic temperature control, limited filament compatibility, manual feed systems | Children, beginners, casual users |
| Mid-Range | $50-$100 | Adjustable speed settings, LCD displays, wider filament compatibility | Hobbyists, educators, intermediate artists |
| Professional | $100-$200+ | Precision temperature control, ergonomic design, advanced material compatibility | Professional artists, designers, engineers |
| Specialty | $80-$250 | Low-temperature models for children, dual-extrusion capabilities, or integration with other systems | Specific use cases like classroom settings or professional applications |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
3D pens have democratized three-dimensional creation, bringing what was once exclusively industrial technology into homes, schools, and studios worldwide. Their intuitive operation makes complex spatial creation accessible to users of all ages and skill levels. As materials science advances and the technology continues to refine, we can expect 3D pens to further blur the lines between traditional art forms and digital fabrication. Whether used for educational purposes, professional design, artistic expression, or simply creative play, these tools represent a significant step forward in how we translate imagination into physical reality. The ongoing evolution of 3D pen technology promises to continue expanding the boundaries of what’s possible in three-dimensional creation for years to come.