Understanding Physiotherapy Options and Back Pain Care Services Near You
Back pain is a common health concern affecting people worldwide, and physiotherapy remains one of the most recommended approaches for managing discomfort and improving mobility. This article explores various physiotherapy treatments for back pain, highlights how to access local services, and offers practical advice for those considering professional care. Whether you're dealing with stiffness or chronic discomfort, this guide provides helpful information to support your recovery journey.
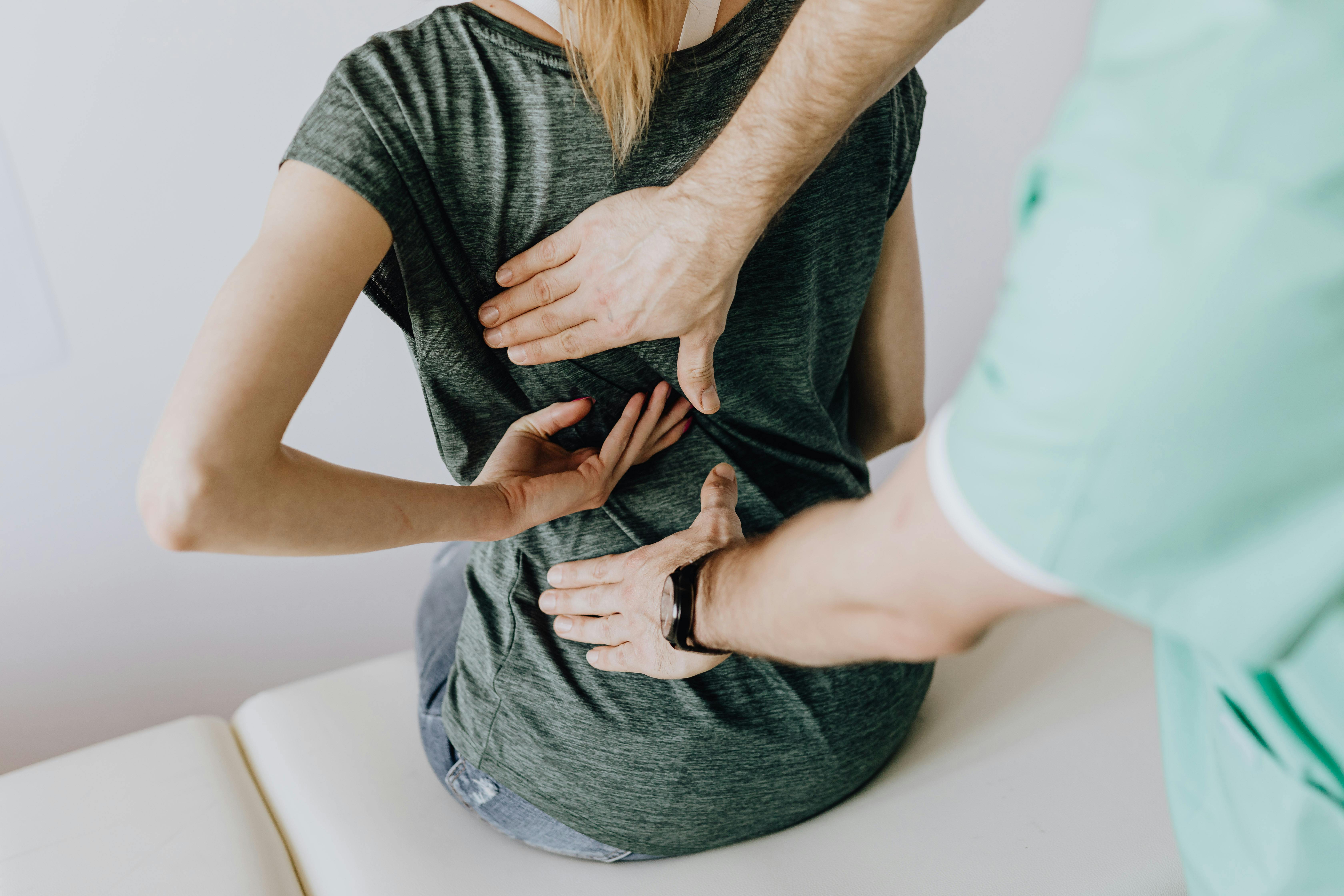

What is physiotherapy and how does it help with back pain?
Physiotherapy is a healthcare profession that focuses on restoring and maintaining physical function, mobility, and overall well-being. When it comes to back pain, physiotherapists use a combination of techniques to address the root causes of discomfort, improve flexibility, and strengthen supporting muscles. These treatments may include manual therapy, exercises, and education on proper body mechanics. By targeting the specific issues causing your back pain, physiotherapy can help reduce pain intensity, improve range of motion, and prevent future injuries.
Which physiotherapy techniques are most effective for back pain?
Several physiotherapy techniques have shown promising results in managing back pain. Manual therapy, which includes massage, joint mobilization, and manipulation, can help alleviate muscle tension and improve spinal alignment. Exercise therapy, tailored to your specific condition, aims to strengthen core muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance overall posture. Other effective techniques include:
- Electrotherapy (TENS, ultrasound)
- Heat and cold therapy
- Acupuncture or dry needling
- McKenzie method for spinal issues
- Hydrotherapy
Your physiotherapist will assess your condition and create a personalized treatment plan using the most appropriate techniques for your needs.
How can I find a qualified back pain specialist or physiotherapist in my area?
Finding a qualified back pain specialist or physiotherapist in your local area is crucial for effective treatment. Start by asking your primary care physician for recommendations. Many healthcare providers have networks of trusted specialists they can refer you to. You can also use online directories provided by professional physiotherapy associations in your country or region. These directories often allow you to search by location and specialty.
Another option is to check with your health insurance provider for a list of in-network physiotherapists who specialize in back pain. Don’t hesitate to ask potential providers about their experience with back pain cases similar to yours and their treatment approaches.
What should I expect during my first physiotherapy session for back pain?
Your first physiotherapy session for back pain typically involves a comprehensive assessment of your condition. The physiotherapist will ask about your medical history, current symptoms, and how the pain affects your daily activities. They will perform a physical examination to assess your posture, range of motion, and strength.
Based on this evaluation, your physiotherapist will develop a personalized treatment plan and discuss it with you. They may start with some initial treatments during this session and provide you with exercises or stretches to do at home. Be prepared to answer questions about your lifestyle and work environment, as these factors can contribute to back pain.
Are there any practical tips for managing back pain and improving mobility at home?
While professional physiotherapy is essential for managing back pain, there are several practical tips you can implement at home to support your treatment and improve mobility:
- Maintain good posture throughout the day, especially when sitting for long periods
- Use proper lifting techniques, bending at the knees and hips rather than the back
- Perform gentle stretches and exercises recommended by your physiotherapist regularly
- Apply heat or cold therapy as advised by your healthcare provider
- Invest in an ergonomic chair and mattress to support your spine
- Stay active with low-impact exercises like walking or swimming
- Practice stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing or meditation
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers as recommended by your doctor
Remember to consult your physiotherapist or doctor before starting any new exercise routine or treatment at home.
How do physiotherapy treatments differ for chronic versus acute back pain?
Physiotherapy treatments for chronic and acute back pain differ in their approach and intensity. Understanding these differences can help you set realistic expectations for your treatment plan.
| Type of Back Pain | Treatment Approach | Duration | Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Back Pain | Short-term, intensive | 2-6 weeks | Pain relief, restoring function |
| Chronic Back Pain | Long-term, progressive | Months to ongoing | Pain management, lifestyle changes |
For acute back pain, treatments often focus on immediate pain relief and restoring normal function. This may involve more hands-on techniques like manual therapy and specific exercises to address the immediate cause of pain.
Chronic back pain management takes a more holistic approach, combining physical treatments with education on pain management strategies, lifestyle modifications, and long-term exercise programs. The goal is to improve overall function and quality of life while managing ongoing pain.
Physiotherapy offers a range of effective treatments for both acute and chronic back pain. By understanding the different approaches and working closely with a qualified physiotherapist, you can develop a personalized plan to manage your back pain and improve your overall well-being. Remember to be patient with the process, as recovery times can vary depending on the severity and cause of your back pain.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
The shared information of this article is up-to-date as of the publishing date. For more up-to-date information, please conduct your own research.