Tinnitus Relief Options in the U.S.: What You Need to Know
For millions of Americans, tinnitus — often experienced as a persistent ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the ears — can interfere with daily life. Whether you're searching for how to stop ringing in the ear or exploring over-the-counter solutions, understanding your options is the first step toward effective symptom management.
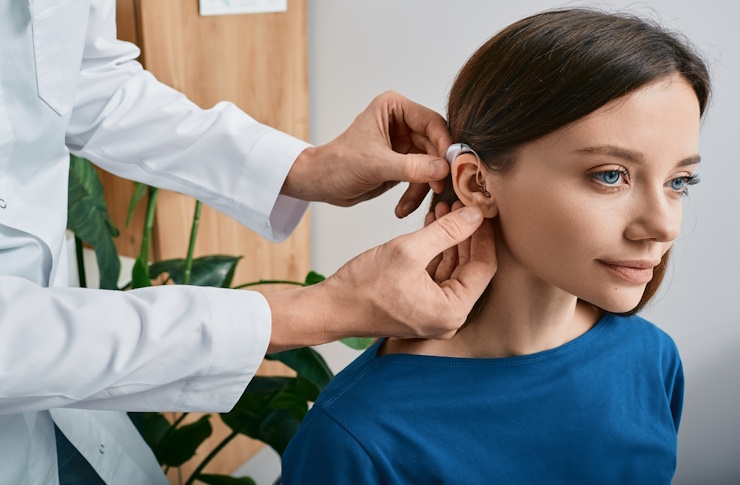
What is tinnitus and what causes it?
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no external noise is present. It’s often described as ringing in the ears, but it can also manifest as buzzing, hissing, whistling, or other phantom sounds. Common causes of tinnitus include:
-
Exposure to loud noises
-
Age-related hearing loss
-
Earwax blockage
-
Certain medications
-
Head or neck injuries
-
Cardiovascular problems
Understanding the underlying cause of your tinnitus is crucial for determining the most effective treatment approach. While tinnitus itself is not a condition but a symptom, identifying its root cause can help guide management strategies.
What medical approaches are available for tinnitus relief?
Medical interventions for tinnitus vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. Some common medical approaches include:
-
Hearing aids: For tinnitus associated with hearing loss, hearing aids can amplify external sounds, making the tinnitus less noticeable.
-
Sound therapy: This involves using external noise to alter the perception of or reaction to tinnitus. Devices like white noise machines or smartphone apps can be used.
-
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This psychological approach helps patients change their perception of tinnitus, reducing its impact on daily life.
-
Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT): Combining sound therapy and counseling, TRT aims to habituate the brain to tinnitus sounds.
-
Medications: While there’s no FDA-approved drug specifically for tinnitus, some medications may help manage related problems like anxiety or depression.
What over-the-counter options are available for tinnitus support?
Several over-the-counter options claim to provide tinnitus relief, though their effectiveness can vary:
-
Dietary supplements: Some people report improvement with supplements like ginkgo biloba, zinc, or B vitamins. However, scientific evidence for their efficacy is limited.
-
Ear drops: Certain OTC ear drops claim to reduce tinnitus symptoms, but their effectiveness is not well-established.
-
Tinnitus maskers: These wearable devices produce white noise or other sounds to mask tinnitus.
-
Herbal remedies: Some herbal preparations are marketed for tinnitus relief, but their efficacy and safety are not well-studied.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement or treatment regimen.
What coping strategies can help manage ringing in the ear?
While medical treatments are important, developing coping strategies can significantly improve quality of life for those with tinnitus:
-
Sound enrichment: Use background noise like fans, soft music, or nature sounds to mask tinnitus.
-
Relaxation techniques: Stress can exacerbate tinnitus. Practices like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga may help.
-
Sleep hygiene: Good sleep habits can reduce the impact of tinnitus, especially at night.
-
Avoid triggers: Identify and avoid things that worsen your tinnitus, such as certain foods, loud noises, or stressful situations.
-
Join support groups: Connecting with others who have tinnitus can provide emotional support and practical tips.
Can tinnitus relief be instant?
While some treatments may provide quick relief, instant and complete tinnitus relief is rare. Most effective treatments work over time:
-
Sound masking devices can provide immediate, though temporary, relief.
-
Some people report quick improvement with certain medications, but results vary.
-
Techniques like focusing on external sounds or engaging in absorbing activities can offer momentary relief.
-
Long-term strategies like TRT or CBT typically show results over weeks or months.
It’s important to have realistic expectations and work with healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive management plan.
When should you see a specialist for tinnitus?
While occasional, brief episodes of tinnitus are common, you should consult a specialist if:
-
Your tinnitus is persistent (lasting more than a few weeks) or severe.
-
Tinnitus is affecting your quality of life, sleep, or concentration.
-
You experience sudden hearing loss along with tinnitus.
-
Your tinnitus is accompanied by dizziness or balance problems.
-
You have pulsatile tinnitus (tinnitus that beats in time with your pulse).
An ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) doctor or an audiologist can provide a thorough evaluation and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Tinnitus can be a challenging condition, but with the right approach, many people find effective ways to manage their symptoms. From medical interventions to lifestyle changes, the key is to work with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan. Remember, while there may not be a cure for all cases of tinnitus, there are many ways to reduce its impact on your daily life.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.