Neurological Disorder Treatment Understanding Modern Options for Better Care
Neurological disorders affect millions of people around the world, impacting movement, memory, balance, speech, and overall quality of life. Conditions such as neuropathy, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, migraines, or chronic nerve pain often require long-term care. Today, thanks to advances in medicine and technology, patients have access to more effective diagnostic tools and treatment options than ever before.
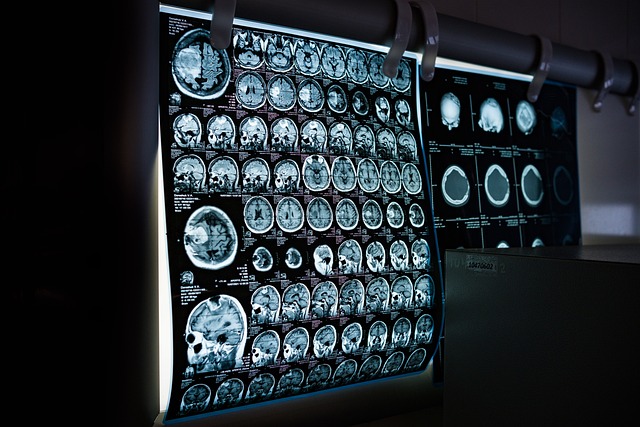
Modern medicine has made remarkable advances in understanding and treating neurological disorders, offering hope and improved outcomes for patients across the United States. These conditions, which affect the central and peripheral nervous systems, range from relatively common issues to rare, complex diseases that require highly specialized care.
What Are Neurological Disorders?
Neurological disorders encompass a broad category of medical conditions that affect the brain, spinal cord, and nerves throughout the body. These disorders can be congenital, meaning present from birth, or acquired later in life due to injury, infection, or degenerative processes. Common neurological conditions include epilepsy, stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, migraines, and traumatic brain injuries. Each condition presents unique challenges and symptoms, from memory problems and movement difficulties to seizures and chronic pain. The complexity of the nervous system means that symptoms can vary widely between patients, even with the same diagnosis, making personalized treatment approaches essential for optimal care.
When to Consider Seeing a Neurology Specialist
Recognizing when to seek specialized neurological care is crucial for early intervention and better outcomes. Primary care physicians often provide initial evaluation, but certain symptoms warrant consultation with a neurologist. Persistent headaches that change in pattern or intensity, unexplained dizziness or balance problems, memory issues that interfere with daily activities, and sudden changes in coordination or movement should prompt specialist evaluation. Additionally, seizures, numbness or tingling in extremities, speech difficulties, and vision changes require neurological assessment. Family history of neurological conditions may also indicate the need for preventive screening or genetic counseling. Early detection and intervention can significantly impact disease progression and treatment effectiveness in many neurological conditions.
Treatment Options Available Today
Contemporary neurological treatment approaches combine traditional therapies with cutting-edge innovations to address the diverse needs of patients. Medication management remains a cornerstone of treatment, with newer drugs offering improved efficacy and fewer side effects for conditions like epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy play vital roles in rehabilitation and maintaining function. Surgical interventions, including minimally invasive procedures and deep brain stimulation, provide options for patients who don’t respond to conservative treatments. Emerging therapies such as gene therapy, stem cell research, and immunomodulatory treatments show promise for previously untreatable conditions. Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes, exercise programs, and stress management techniques, complement medical treatments and can significantly impact disease progression and symptom management.
Modern Diagnostic Tools
Advanced diagnostic technologies have revolutionized the identification and monitoring of neurological disorders, enabling more precise diagnoses and targeted treatments. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) provides detailed images of brain and spinal cord structures, while functional MRI can assess brain activity in real-time. Computed Tomography (CT) scans offer rapid evaluation, particularly important in emergency situations like stroke or head trauma. Electroencephalography (EEG) monitors electrical activity in the brain, essential for diagnosing epilepsy and other seizure disorders. Nerve conduction studies and electromyography assess peripheral nerve and muscle function. Newer technologies include positron emission tomography (PET) scans for detecting early Alzheimer’s disease changes and cerebrospinal fluid analysis for biomarkers. Genetic testing has become increasingly important for hereditary neurological conditions, allowing for early detection and family planning considerations.
| Provider Type | Services Offered | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Academic Medical Centers | Comprehensive care, research trials | Cutting-edge treatments, multidisciplinary teams |
| Specialized Neurology Clinics | Focused neurological care | Disease-specific expertise, coordinated care |
| Rehabilitation Centers | Physical therapy, occupational therapy | Functional improvement, adaptive equipment |
| Telemedicine Platforms | Remote consultations, monitoring | Accessible care, convenient follow-ups |
The landscape of neurological disorder treatment continues to evolve rapidly, with new research findings and therapeutic approaches emerging regularly. Patient advocacy groups and support networks provide valuable resources for individuals and families navigating these complex conditions. Collaboration between patients, families, and healthcare teams remains essential for developing effective treatment plans that address both medical needs and quality of life concerns. As our understanding of the nervous system deepens, the future holds promise for even more targeted and effective treatments for neurological disorders.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.