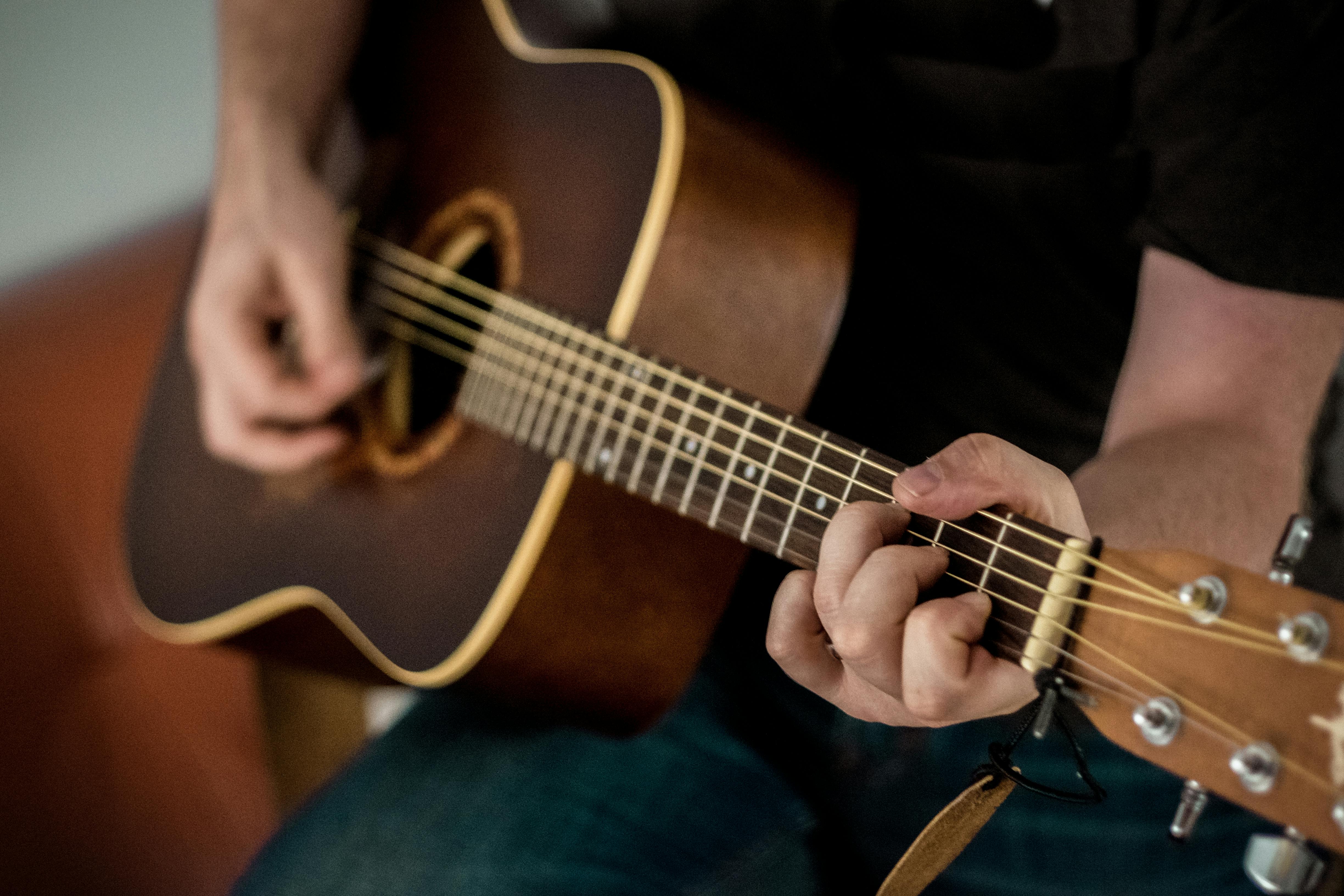
Introduction to Guitar Types and Playing Basics
The guitar is a versatile stringed instrument used in a wide range of musical genres, from classical to rock. It comes in various forms, including acoustic, electric, and classical models—each suited for different playing styles. Learning involves understanding chord structures, strumming techniques, and proper tuning. Regular practice and basic maintenance are key to progress and sound quality.

What are the main types of guitars?
Guitars come in several varieties, each with its unique characteristics and suited for different musical styles. The three primary types of guitars are:
-
Acoustic Guitars: These are the most common and versatile guitars. They produce sound through the vibration of strings amplified by the guitar’s hollow body. Acoustic guitars are ideal for folk, country, and singer-songwriter genres.
-
Electric Guitars: Electric guitars rely on electronic pickups to convert string vibrations into electrical signals, which are then amplified through speakers. They are popular in rock, blues, jazz, and many other contemporary genres.
-
Classical Guitars: Also known as Spanish guitars, these feature nylon strings and a wider neck. Classical guitars are primarily used in classical music, flamenco, and some folk styles.
Each guitar type offers a distinct tonal quality and playing experience, allowing musicians to choose the instrument that best suits their musical preferences and goals.
How do you properly tune a guitar?
Proper tuning is crucial for producing pleasing sounds and playing in harmony with other instruments. Here’s a basic tuning guide for a standard six-string guitar:
-
Use a tuner: Electronic tuners are the most accurate and easiest way to tune your guitar. Clip-on tuners or smartphone apps are readily available.
-
Standard tuning: The strings should be tuned to E, A, D, G, B, E (from the thickest to thinnest string).
-
Start with the low E string: Pluck the string and adjust the tuning peg until the tuner indicates the correct pitch.
-
Move to the next string: Repeat the process for each string, working your way up to the high E string.
-
Fine-tune: After initial tuning, go through all strings again to make minor adjustments, as tuning one string can slightly affect the others.
-
Use relative tuning: Once familiar with standard tuning, you can tune by ear using the 5th fret method, comparing adjacent strings.
Remember, regular tuning is essential for maintaining your guitar’s sound quality and playability.
What are the fundamental playing basics for beginners?
Mastering the basics is crucial for developing proper technique and progressing as a guitarist. Here are some fundamental playing basics to focus on:
-
Proper posture: Sit or stand comfortably with your back straight and the guitar resting on your leg or supported by a strap.
-
Fretting hand position: Place your thumb behind the neck and use your fingertips to press the strings against the fretboard.
-
Picking hand technique: Whether using a pick or your fingers, maintain a relaxed grip and practice consistent strumming or plucking motions.
-
Basic chords: Learn open chords like A, D, G, C, and Em, which are foundational for many songs.
-
Strumming patterns: Start with simple down-strums and gradually introduce more complex patterns.
-
Reading tablature: Familiarize yourself with guitar tabs, a simplified form of music notation for guitarists.
-
Practicing scales: Begin with the major scale to develop finger dexterity and understand musical theory.
Consistent practice of these fundamentals will build a strong foundation for your guitar-playing journey.
How can you effectively practice guitar chords?
Chord practice is essential for developing muscle memory and transitioning smoothly between different chord shapes. Here are some effective chord practice techniques:
-
Start slow: Begin with basic open chords and practice transitioning between them at a slow, comfortable pace.
-
Use a metronome: Gradually increase your speed while maintaining proper form and clear sound.
-
Practice chord progressions: Learn common progressions like C-G-Am-F to build practical skills for playing songs.
-
Implement the one-minute changes exercise: Set a timer for one minute and see how many times you can switch between two chords.
-
Focus on problem areas: Identify challenging chord transitions and dedicate extra practice time to them.
-
Play along with songs: Apply your chord knowledge to real music, starting with simple songs and progressing to more complex ones.
-
Explore barre chords: Once comfortable with open chords, introduce barre chords to expand your repertoire.
Remember, consistency is key. Even short, regular practice sessions can lead to significant improvement over time.
What are some essential care tips for maintaining your guitar?
Proper guitar care is crucial for maintaining your instrument’s sound quality, playability, and longevity. Here are some essential care tips:
-
Clean your guitar regularly: Wipe down the strings, fretboard, and body after each playing session to remove dirt and oils.
-
Store properly: Keep your guitar in a case or on a stand in a room with stable temperature and humidity.
-
Change strings periodically: Replace strings when they become dull or difficult to tune, typically every 3-6 months for regular players.
-
Adjust humidity: Use a humidifier or dehumidifier to maintain optimal humidity levels (45-55%) to prevent warping or cracking.
-
Polish and condition: Use guitar-specific products to clean and protect the wood finish.
-
Check for loose parts: Regularly inspect and tighten any loose tuning pegs, bridge pins, or screws.
-
Professional setup: Consider having a professional setup done annually to ensure optimal playability and sound quality.
By following these care tips, you’ll ensure that your guitar remains in top condition for years of enjoyable playing.
How do different guitar types affect playing styles and techniques?
Different guitar types cater to various playing styles and techniques, influencing the musician’s approach and sound. Here’s a comparison of how guitar types impact playing:
| Guitar Type | Playing Style | Techniques | Typical Genres |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acoustic | Fingerpicking, strumming | Palm muting, percussive techniques | Folk, country, singer-songwriter |
| Electric | Lead playing, power chords | Bending, tapping, use of effects pedals | Rock, blues, jazz, metal |
| Classical | Fingerstyle, arpeggios | Tremolo, rasgueado | Classical, flamenco, bossa nova |
Acoustic guitars often require a stronger attack and are well-suited for both fingerpicking and strumming techniques. Their resonant bodies make them ideal for solo performances and songwriting.
Electric guitars offer greater versatility in sound manipulation through amplification and effects. They allow for techniques like string bending and tapping, which are essential in many rock and blues styles.
Classical guitars, with their wider necks and nylon strings, facilitate complex fingerstyle techniques and are preferred for classical and flamenco music.
Understanding these differences can help guitarists choose the right instrument for their preferred style and explore new musical territories.
In conclusion, embarking on your guitar-playing journey involves understanding different guitar types, mastering tuning techniques, practicing fundamental skills, and maintaining your instrument. By focusing on these aspects and consistently practicing, you’ll develop the foundation needed to express yourself musically and enjoy the rewarding experience of playing the guitar. Remember, every great guitarist started as a beginner, so be patient with yourself and enjoy the learning process.