Blood Sugar Level
Blood sugar level is the amount of glucose found in the blood. Levels can change at different times of the day. These changes may be related to meals, physical movement, or other daily activities. Blood sugar can be checked using approved devices that measure glucose in a small blood sample.
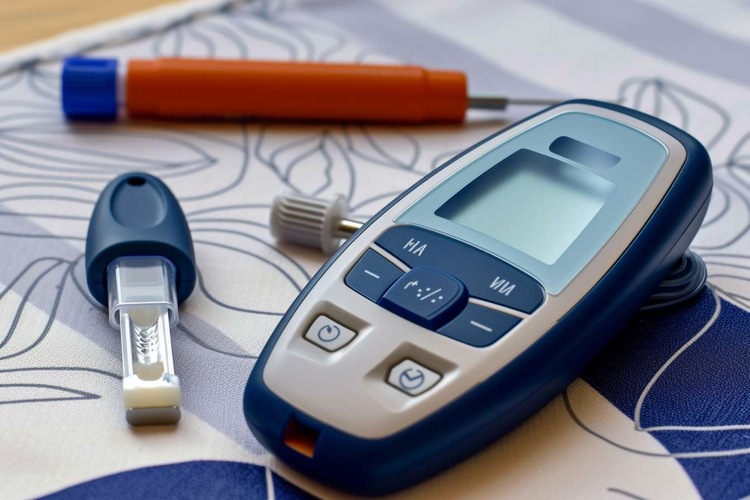

What Is Blood Sugar Level?
Blood sugar level refers to the amount of glucose present in your bloodstream at any given time. Glucose is the primary source of energy for your body’s cells, and its concentration in the blood is tightly regulated by various hormones, primarily insulin. Normal blood sugar levels typically range between 70 and 99 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) when fasting, and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating.
Why Does Blood Sugar Change During the Day?
Blood sugar levels naturally fluctuate throughout the day in response to various factors. The most significant influence comes from food consumption, particularly carbohydrates, which are broken down into glucose during digestion. After eating, blood sugar levels rise as glucose enters the bloodstream. In response, the pancreas releases insulin to help cells absorb and use this glucose, bringing blood sugar levels back down.
Other factors that can cause blood sugar changes include:
- Physical activity: Exercise can lower blood sugar as muscles use glucose for energy.
- Stress: Stress hormones can cause blood sugar to rise.
- Medications: Certain drugs, like corticosteroids, can increase blood sugar.
- Illness: Being sick can affect blood sugar levels, often causing them to rise.
- Hormonal changes: Menstrual cycles or pregnancy can impact blood sugar levels.
How to Monitor Blood Sugar Effectively
Monitoring blood sugar is a straightforward process that can be done at home or in a clinical setting. The most common method is using a blood glucose meter, also known as a glucometer. Here’s how it typically works:
- Wash and dry your hands thoroughly.
- Insert a test strip into the glucose meter.
- Use a lancet to prick the side of your fingertip.
- Gently squeeze your finger to produce a small drop of blood.
- Touch the edge of the test strip to the blood drop.
- Wait for the meter to display your blood sugar reading.
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems are also available, which use a tiny sensor inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels in interstitial fluid every few minutes throughout the day and night.
When Is Blood Sugar Monitoring Recommended?
Regular blood sugar monitoring is recommended for people with diabetes, as it helps manage the condition and prevent complications. However, there are other situations where monitoring may be advised:
- Prediabetes: People at risk of developing type 2 diabetes may benefit from occasional monitoring.
- Pregnancy: Women with gestational diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar regularly.
- Certain medications: Some medications can affect blood sugar levels and may require monitoring.
- After surgery or during illness: These situations can temporarily affect blood sugar levels.
- Unexplained symptoms: If you experience symptoms like frequent urination, excessive thirst, or unexplained weight loss, your doctor may recommend monitoring.
What Do Blood Sugar Readings Mean?
Understanding your blood sugar readings is crucial for effective management. Here’s a general guide:
- Fasting blood sugar (8 hours without food):
- Normal: Less than 100 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100-125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal:
- Normal: Less than 140 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 140-199 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 200 mg/dL or higher
It’s important to note that target ranges can vary based on individual factors, and your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate range for you.
How Can You Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels?
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle choices and, in some cases, medication. Here are some effective strategies:
- Balanced diet: Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
- Regular exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Stress management: Practice relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing.
- Adequate sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Medication adherence: If prescribed, take diabetes medications as directed by your healthcare provider.
Blood sugar monitoring devices and supplies can vary in cost. Here’s a general comparison of some common options:
| Product Type | Brand Example | Approximate Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Glucose Meter | Accu-Chek Active | $20 - $50 |
| Test Strips (50 count) | OneTouch Ultra | $30 - $60 |
| Lancets (100 count) | Microlet | $5 - $15 |
| Continuous Glucose Monitor | Dexcom G6 | $300 - $500 (initial cost) |
| CGM Sensors (1 month supply) | FreeStyle Libre | $100 - $200 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Understanding and managing blood sugar levels is a vital aspect of overall health, particularly for those at risk of or living with diabetes. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits and monitoring when necessary, you can take control of your blood sugar and promote long-term well-being.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
The shared information of this article is up-to-date as of the publishing date. For more up-to-date information, please conduct your own research.