Approaches to Migraine Management and Relief
Migraine treatment involves strategies aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of symptoms. Options may include lifestyle adjustments, medical evaluation, and the use of prescribed or over-the-counter therapies. Understanding potential triggers and response plans can support individuals in managing recurring episodes.
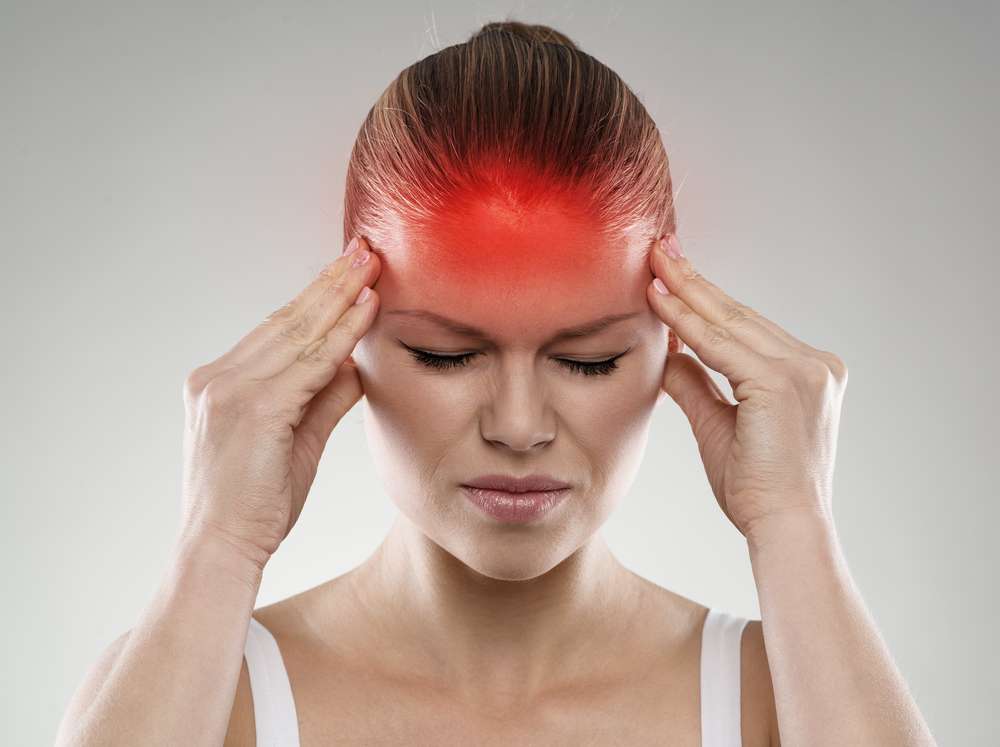

What are the common symptoms of migraines?
Recognizing migraine symptoms is crucial for proper management. Typical signs include:
- Intense, throbbing headache, often on one side of the head
- Sensitivity to light, sound, and sometimes smells
- Nausea and vomiting
- Visual disturbances (aura) in some cases
- Dizziness and fatigue
These symptoms can last from a few hours to several days. Some individuals may experience warning signs, like mood changes or food cravings, before a migraine attack.
What medical options are available for migraine treatment?
Medical management of migraines typically involves two approaches: acute treatment and preventive therapy.
Acute treatments aim to stop migraine symptoms once they start. Options include:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen, aspirin)
- Prescription medications like triptans or ergotamines
- Anti-nausea drugs
Preventive therapies are used to reduce the frequency and severity of migraines. These may include:
- Beta-blockers
- Antidepressants
- Anti-seizure medications
- CGRP antagonists
A healthcare provider can help determine the most suitable treatment plan based on individual symptoms and medical history.
What non-medical approaches can help manage migraines?
Non-medical management strategies play a crucial role in migraine relief:
- Stress reduction techniques (e.g., meditation, yoga)
- Regular exercise
- Consistent sleep schedule
- Dietary modifications
- Acupuncture or massage therapy
- Biofeedback
Combining these approaches with medical treatments often yields the best results. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive management plan.
How can migraine triggers be identified and avoided?
Identifying and avoiding triggers is key to migraine prevention. Common triggers include:
- Certain foods (e.g., aged cheeses, alcohol, chocolate)
- Hormonal changes
- Weather changes
- Bright lights or loud noises
- Lack of sleep or irregular sleep patterns
Keeping a migraine diary can help identify personal triggers. Record details about each migraine episode, including potential triggers, symptoms, and duration. This information can guide prevention strategies and assist healthcare providers in refining treatment plans.
When should someone seek clinical evaluation for migraines?
While occasional headaches are common, certain situations warrant medical attention:
- Headaches that significantly interfere with daily life
- Migraines that don’t respond to over-the-counter treatments
- Changes in headache patterns or intensity
- New onset of severe headaches, especially after age 50
- Headaches accompanied by neurological symptoms (e.g., vision changes, weakness)
- Migraines occurring with pregnancy or certain medical conditions
A healthcare provider can perform a thorough evaluation, rule out other conditions, and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
How do daily habits influence migraine patterns?
Daily habits can significantly impact migraine frequency and severity. Consider incorporating these practices:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day
- Eat regular, balanced meals to maintain stable blood sugar levels
- Practice good posture to reduce neck and shoulder tension
- Limit caffeine intake and avoid sudden caffeine withdrawal
- Use screens mindfully and take regular breaks to reduce eye strain
- Engage in relaxation techniques daily, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation
Consistency in these habits can help reduce the likelihood of triggering a migraine attack and improve overall well-being.
While migraine management often involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions, some individuals may benefit from specialized treatments or devices. Here’s a comparison of some options:
| Treatment/Device | Provider | Key Features | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Botox Injections | Neurologists, Pain Specialists | Reduces muscle tension, FDA-approved for chronic migraines | $300-$600 per session |
| CGRP Inhibitors | Prescription medication | Monthly self-administered injections, targets specific migraine pathways | $500-$700 per month |
| Transcutaneous Supraorbital Neurostimulation | Cefaly | Wearable device, stimulates trigeminal nerve | $250-$500 for device |
| Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation | eNeura | Non-invasive brain stimulation, FDA-approved for migraine with aura | Rental: $150-$250 per month |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
In conclusion, effective migraine management often requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding symptoms, identifying triggers, and exploring various treatment options, individuals can work towards reducing the impact of migraines on their daily lives. Regular communication with healthcare providers is essential for optimizing treatment strategies and improving overall quality of life.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
The shared information of this article is up-to-date as of the publishing date. For more up-to-date information, please conduct your own research.